|
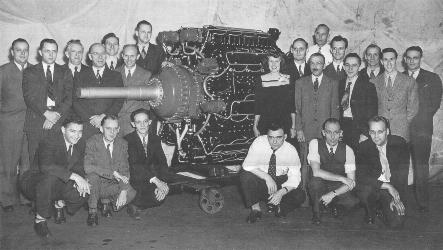
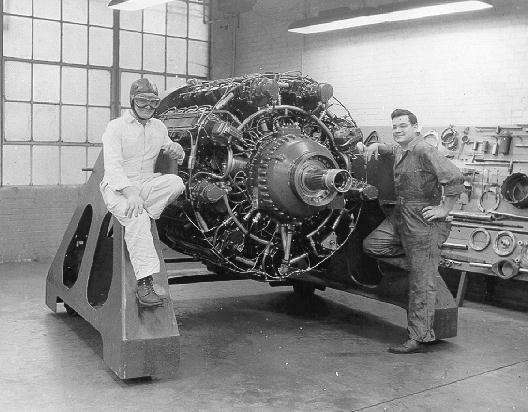
The XR-7755, 36-cylinder engine was destined to be the largest reciprocating engine ever built. The displacement was 7,755 cubic inches. When compared to Lycoming's largest production engine in production today which displaces 720 cubic inches, it was more than 10 times larger!
The huge engine was 10 feet long, 5 feet in diameter and weighed 6,050 pounds. It produced 5,000 hp at 2,600 rpm, and the target was 7,000 hp. It used 580 gph of aviation gas at the 5,000 hp rating. |
|
There were nine overhead camshafts which could be shifted axially for METO power in one position and cruise at the other. Two great shafts emerged for coaxial propellers, and there was a two speed gear-change box between the crankshaft and the propeller shafts.
Development of the XR-7755 began at Lycoming in Williamsport in the summer of 1943. With the end of World War II in 1945, the military no longer had a need for an engine of this size, and development of the XR-7755 stopped at the prototype stage. During those years, Lycoming put together a team, under the leadership of VP Engineering Clarence Wiegman, to develop this super-size engine. The engine now resides at Silver Hill of the Smithsonian Institute.
|
| Lycoming XR-7755 | |
|---|---|
| Specifications: | |
| Date: | 1943 |
| Displacement: | 7,755 cu. in. (127 liters) |
| Cylinders: | 36 |
| Bore and Stroke:: | 6.4 in. (162 mm) x 6.8 in. (171 mm) |
| Weight: | 6,050 lbs. (2,744 kg) |
| Performance: | |
| Horsepower: | 5,000 hp (3,728 kw) at 44 in Hg.MP. |
| RPM: | 2,600 |
| Configuration: | |
|
4-cycle, 4 row radial, liquid cooled, 2 speed geared dual rotation propeller drive with turbo-supercharger. | |
© The Aviation History On-Line Museum. All rights reserved.
Created November 11, 2001. Updated October 12, 2013.